Facilities
VIDEO E.E.G
A video EEG (electroencephalograph) records what you are doing or experiencing on video tape while an EEG test records your brainwaves. The purpose is to be able to see what is happening when you have a seizure or event and compare the picture to what the EEG records at the same time. Sounds that occur during the testing are also recorded – this can pick up if a person talks or makes sounds during an event. By doing this, doctors reading the EEG can tell if the seizure or event was related to the electrical activity in the brain. If so, we’d call this an epilepsy seizure.

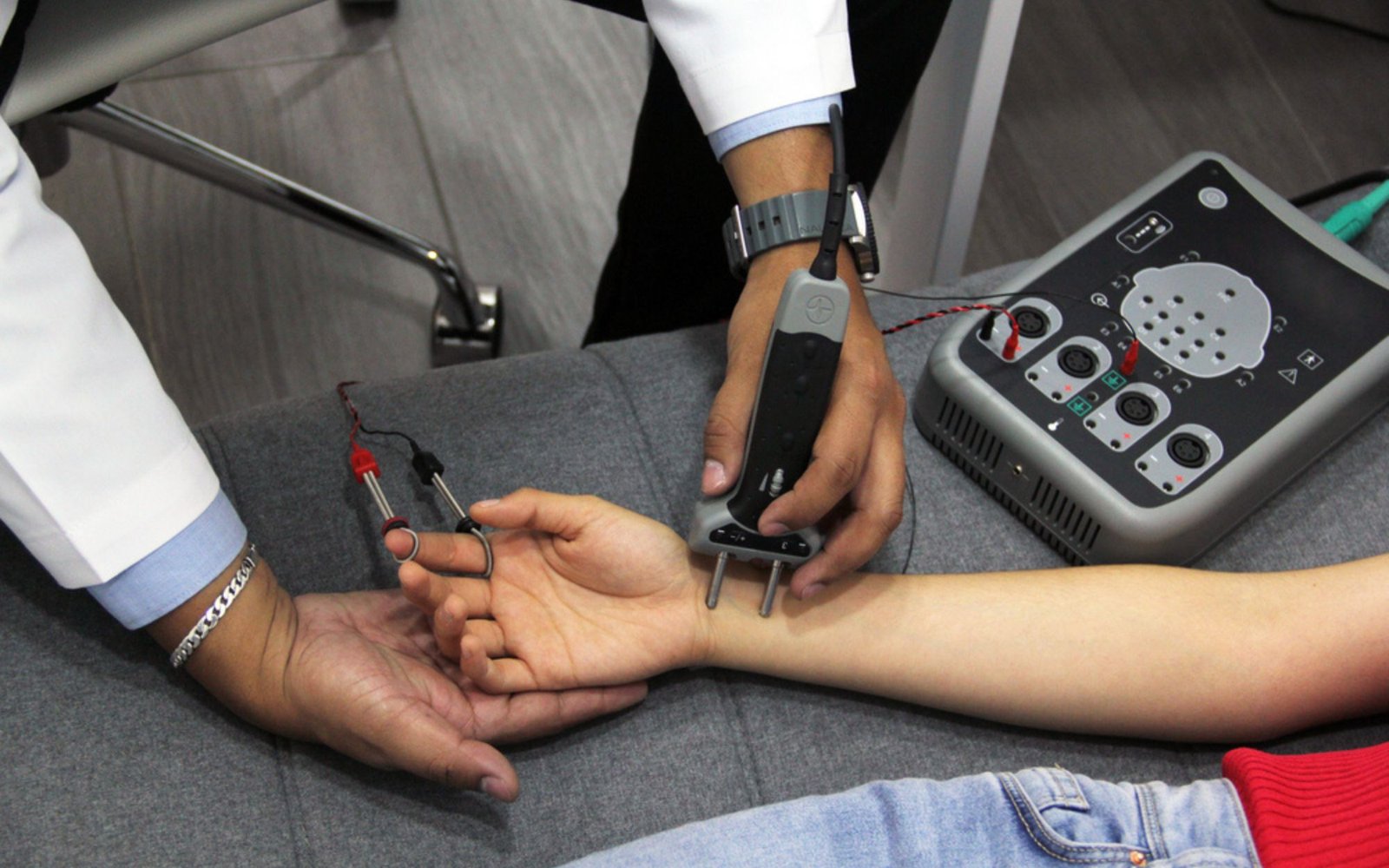
Nerve Conduction Studies
Nerve conduction studies show whether the nerves transmit electrical impulses to the muscles or up the sensory nerves at normal speeds (conduction velocities). Sensory nerves allow the brain to respond to pain, touch, temperature and vibration. Different nerves have different normal conduction velocities. Nerve conduction velocities also tend to decrease as a person gets older. Slower conduction velocities may also be caused by injury or damage to a nerve (such as carpal tunnel syndrome) or group of nerves (such as Guillain-Barré syndrome or post-polio syndrome).
Empty heading
Empty heading
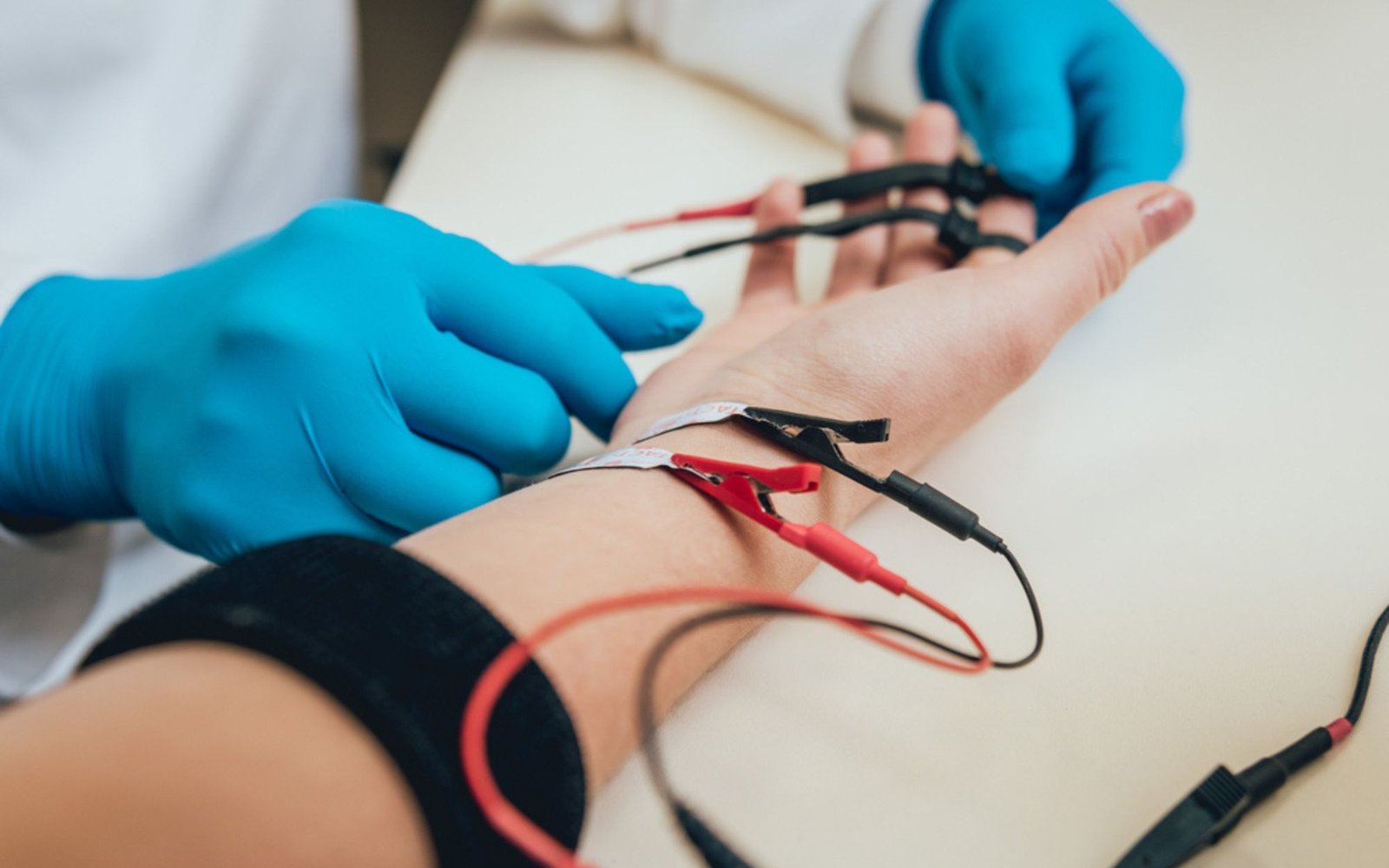
Nerve and Muscle Test
To evaluate individual motor units within a muscle, an electrode must be placed into the muscle itself. Needle electrodes used for this purpose will be described below. As with all work involving electrical equipment, a ground electrode must be used and should be placed on the same extremity that is being investigated. For grounding, a plate electrode is the most useful and best tolerated by the patient, though uninsulated needles have been used. The electromyographer chooses the type of needle electrode to use, and it is preferable that he or she uses one type consistently to become well acquainted with its characteristics.
VEP
Visual Evoked Potentials (VEPs) testing measures the signals from your visual pathway. Small gold cups called electrodes are pasted to your head to allow us to record those signals. Just like in a regular eye exam, it is necessary to check how each eye works on its own. This is done by patching the eye that isn’t being checked. If you have glasses, you should bring them for this test.
Autonomic Function Testing
This test includes four separate studies. The first three involve continuous heart rate and blood pressure responses to individual tasks. The heart rate and blood pressure are recorded with electrodes applied to your chest and wrist. The fourth part of the exam involves measuring how much sweat your body produces. Small recording devices are placed onto your forearm, leg and foot. These devices measure your sweat production in response to a very tiny electrical stimulus.

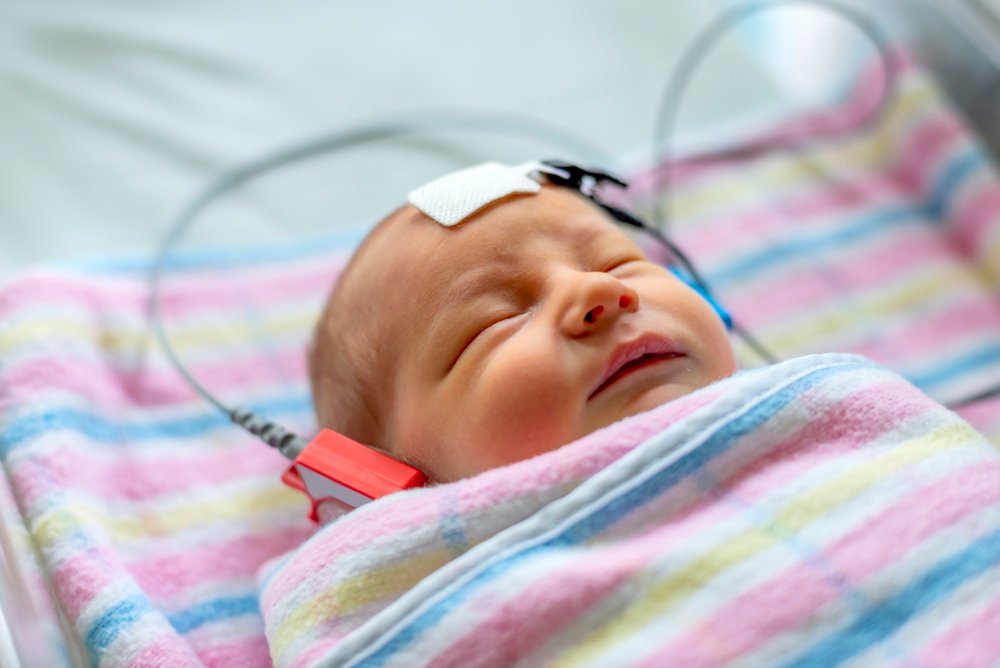
BAER
BAER is commonly performed on newborn infants to screen their hearing and is often used in conjunction with OAE testing. If there are no complications with your child’s delivery, OAE will likely be performed and BAER testing only if OAE is failed. If your child is born premature or has a risk for neurological impairment, BAER testing will be performed first. If your child does not pass BAER testing it does not necessarily mean they are deaf or have permanent hearing loss; further testing is needed. Another common reason BAER testing will be performed is if you have a child with a developmental delay that cannot have other forms of testing done to check their hearing.
